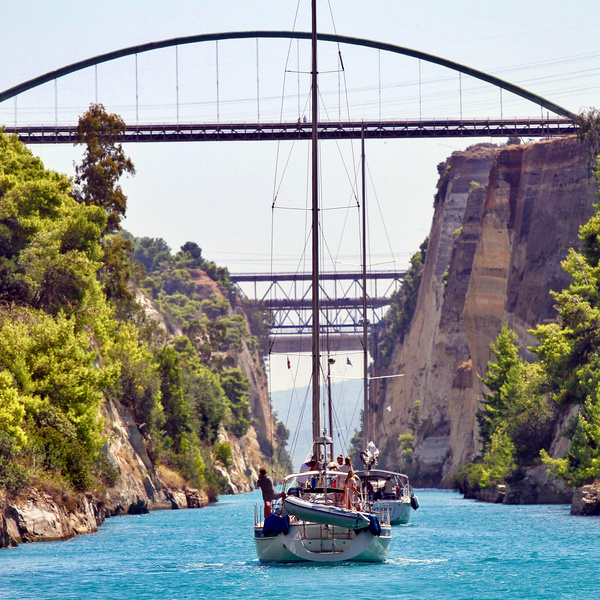
Sailing the Corinth Canal – The Diolkos
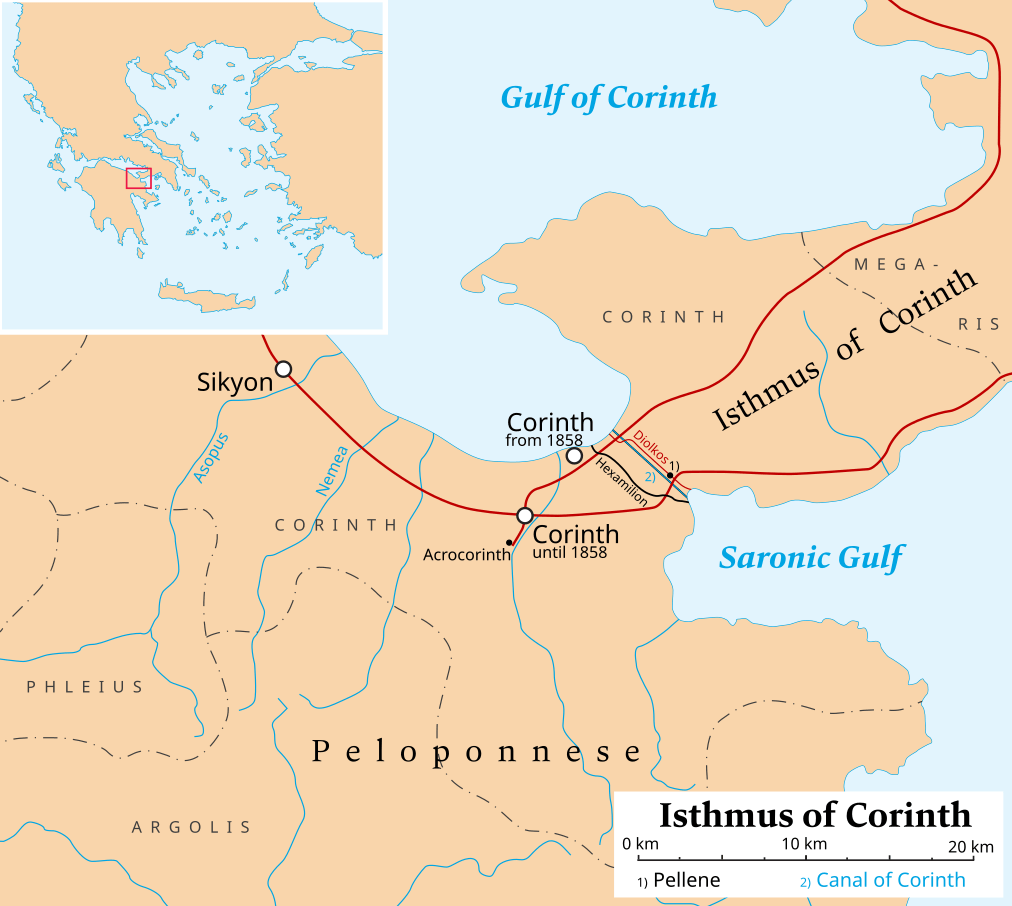
When travelling from Athens to Corinth – a distance of about 80 kilometres – you leave Attica to enter the Peloponnese while crossing an Isthmus, a narrow and fairly low-lying, 3.2 NM wide, tongue of land which links Central Greece (Sterea Ellada) with the Peloponnese as well as with the east parts of the Saronic Gulf.
Both economically and strategically, the Isthmus of Corinth, as this narrow stretch of land is called, has played a very important role in the history of Greece. It is the only land bridge between the country's north and south. Populations, armies and commodities have got to move through it.
This basic fact let to the birth of an important city, Corinth, at its threshold. There were times when the influence of Corinth extended beyond the Saronic Gulf to the Aegean Sea and beyond the Gulf of Corinth to the Adriatic.
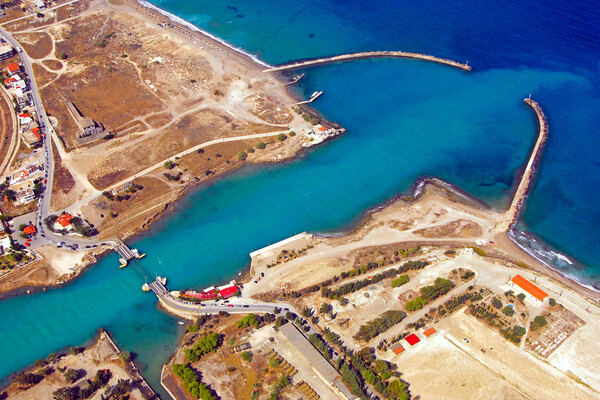
Hence, two important ports made their appearance in antiquity on both sides of the Isthmus – Lechaeum (Lechaion) on the Gulf of Corinth, and Kenchreai on the shores of the Saronic Gulf.
The Corinth Canal - Διώρυγα της Κορίνθου is managed by the Ανώνυμη Εταιρεία Διώρυγας Κορίνθου (Α.Ε.ΔΙ.Κ), and if you want to cross use their “Tolls calculator”; additional tel. +30 2741028511; €280 for a 15m yacht with VAT (check whether VAT is relevant), cash payable on the east side (Isthmia); VHF 11, but ideally check in more than 24 hrs in advance as well as online by credit card.
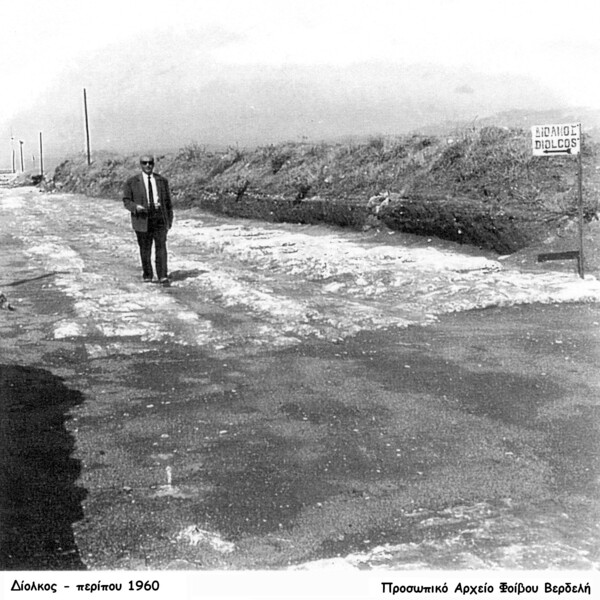
The Diolkos
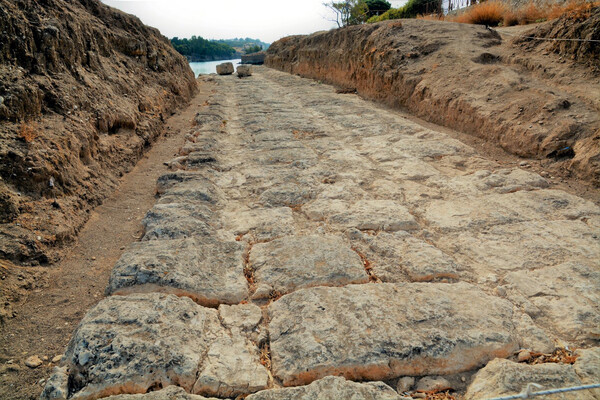
“How to get your ship from the Gulf of Corinth to the Saronic Gulf and vice versa?” This question plagued the seafaring Greeks since very early times. It was first solved towards the end of the 7th c. BCE, or at the beginning of the 6th c., by a daring decision which led to the greatest of technical construction works in early Greece : the building of the Diolkos or “slipway”.
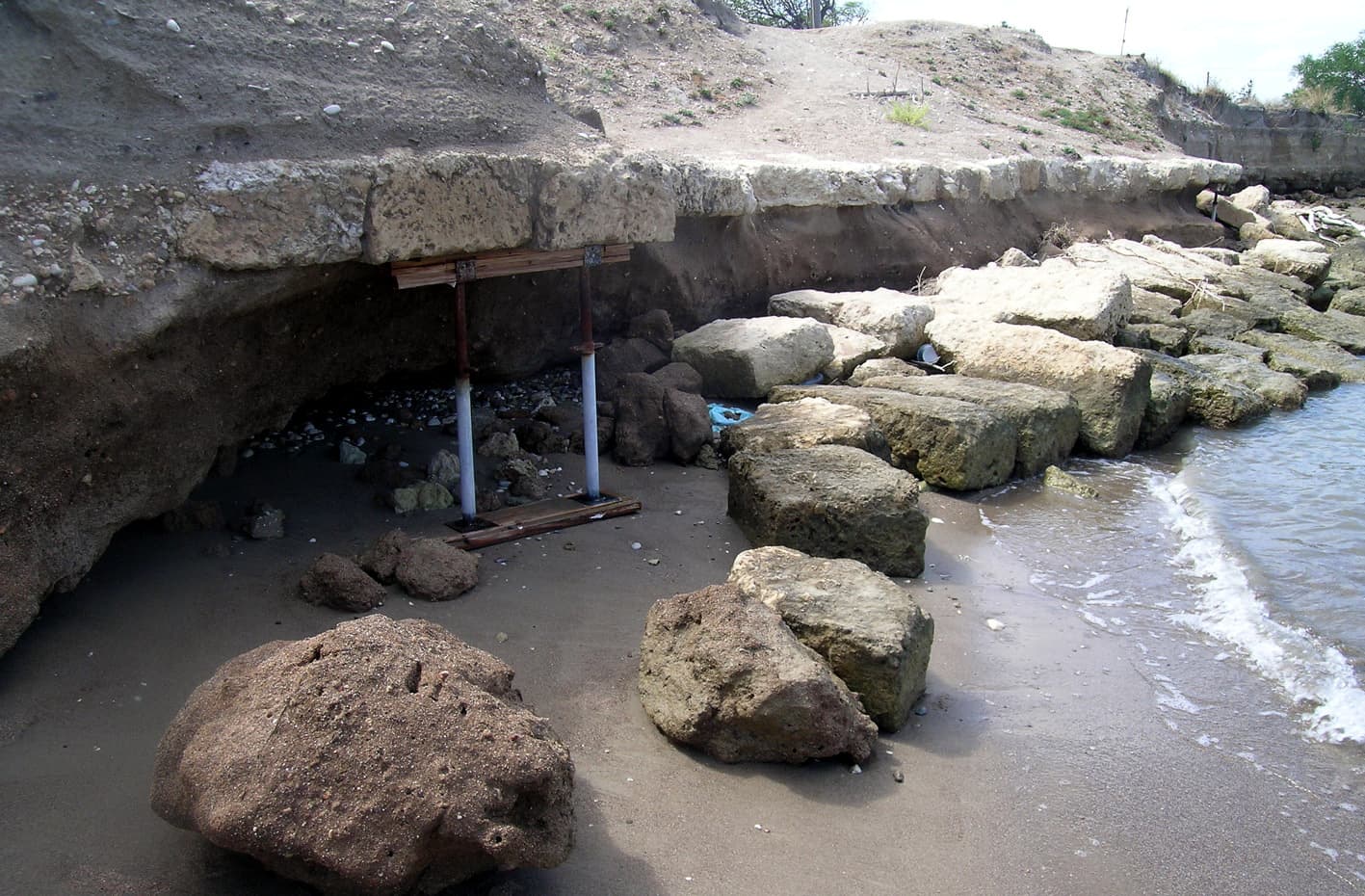

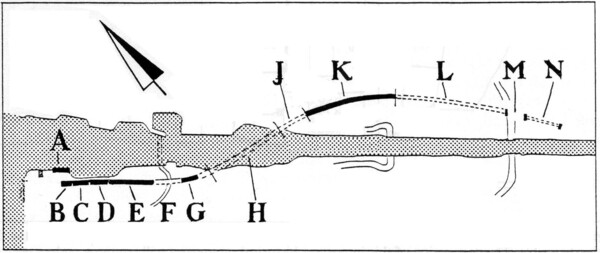
The course of Diolkos which is illustrated below is the one proposed by the Belgian George Raepsaet, yet Walter Werner and others suggest another route, which describes a large curve into the peloponnesian side of the modern canal, before ending in Kalamaki-Isthmia.
Between 1956 and 1959, Nikolaos Verdelis of the Greek Archaeological Society carried out excavations designed to trace the course of the Diolkos. The greater part of the slipway, which obviously had to ran all the way from the Gulf of Corinth to the Saronic Gulf, was brought to light.
The Diolkos was a roadway with a width of 10 meters at the starting point on the Gulf of Corinth. The stone-paving began at the very edge of the sea. Ships were taken to this starting point and there dragged onto the Diolkos. These ships rested initially on wooden cylinders and were then transferred to a special wheeled vehicle.
To reduce the weight of the ship as far as possible, it was unloaded before being hoisted onto the Diolkos and the unloaded commodities were taken by ordinary road to the other end of the Isthmus.
Narrowing to between 3.50 and 6 metres after its starting point the slipway was paved with porous stone throughout its length. Two deep parallel grooves, which ran at a distance of 1.50 metres from each other, marked the Diolkos.
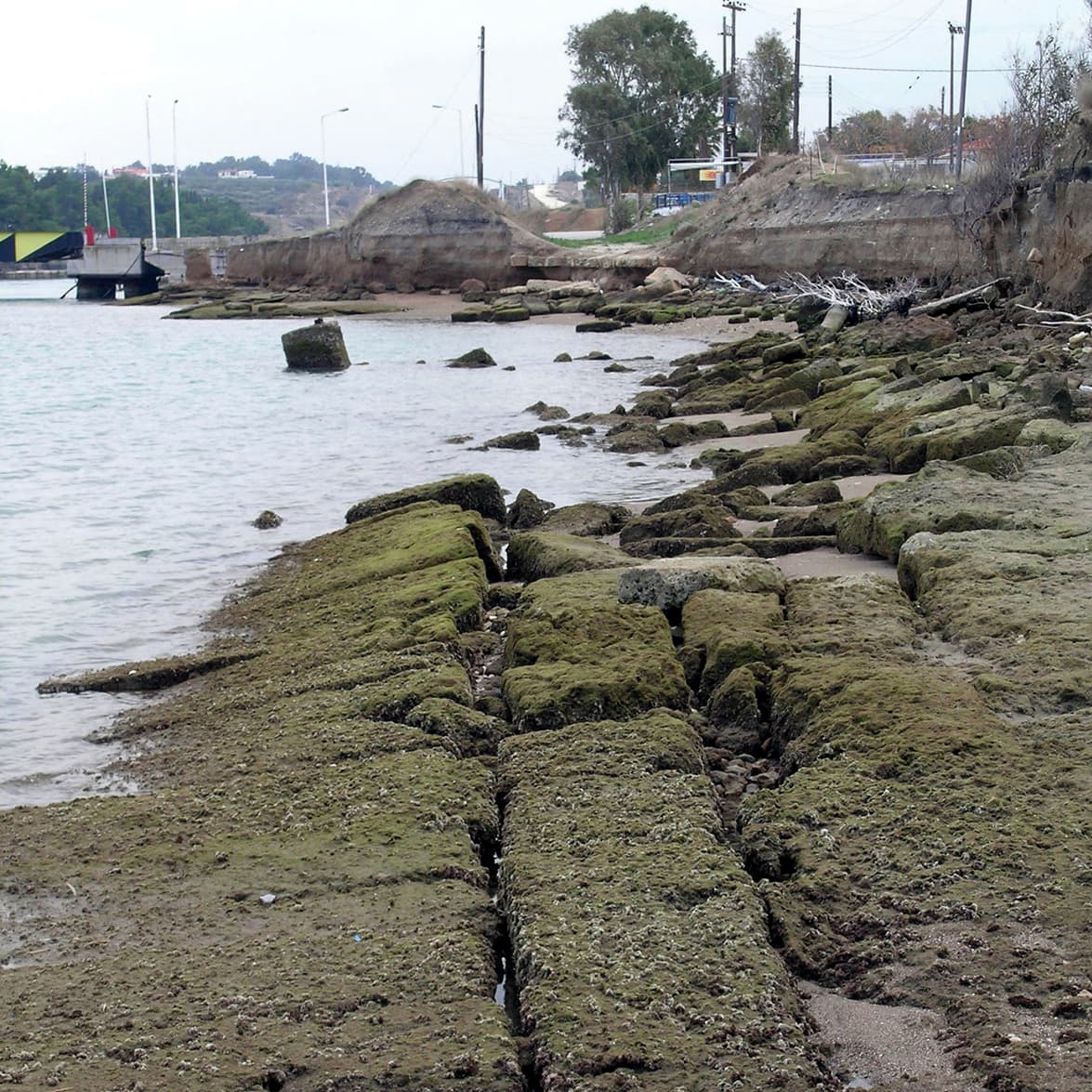

Thus, the ship was dragged all across the Isthmus, and on reaching the slipway's terminus on the Saronic Gulf, it was lowered into the sea, the cargo was loaded again, and the ship continued with its journey.
This arrangement did not merely speed up traffic. It also enabled ships moving between the Central and Eastern Mediterranean to avoid the rough seas almost unavoidable in a voyage round the Peloponnese.
The Diolkos was repeatedly repaired in ensuing centuries and remained in use until the days of Augustus, though the appearance of ever-larger ships curtailed its usefulness. There is hardly any mention of its use in later centuries, and then only in connection with warlike activities.
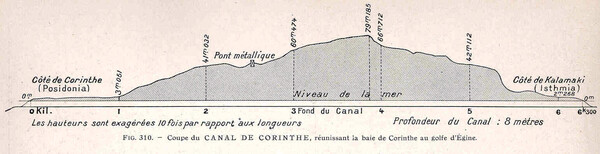
Heights are exaggerated 10 times compared to lengths. On the left the Gulf of Corinth at Posidonia (0 km) and on the right the Saronic Gulf at Kalamaki-Isthmia (6+ km).
Cutting through the Isthmus
The use of the Diolkos was difficult and expensive at all times and proved impossible with larger ships. Hence, in ancient days already, people envisaged cutting a canal across the Isthmus, so as to link the two Gulfs permanently and make it possible for all ships at all times to avoid the dangerous journey past Cape Maleas, off South Peloponnese.
Yet, technical means then available made it in fact impossible to carry through such an ambitious scheme in those early days. It was Emperor Nero who first attempted to cut a canal through the Isthmus. Feasibility studies were completed, the necessary work force was gathered, and Nero in person started the digging with a little golden pickaxe.
Three months later, however, Nero died, and the project was abandoned. 17 centuries later, immediately after the liberation of Greece in the first half of the 19th century, the canal project was revived under Kapodistrias. Its execution hung fire until 1882, when a French firm took the work in hand. It was a Greek firm which completed it in 1893.
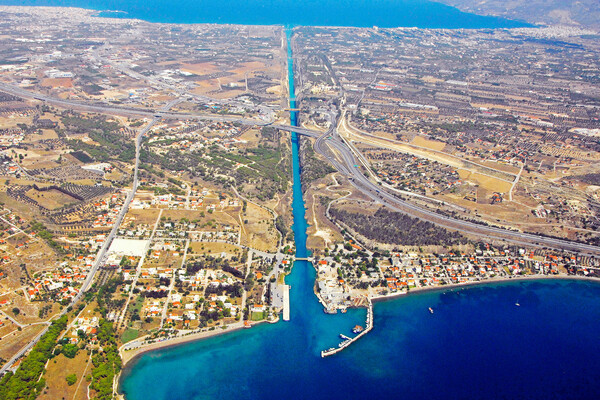
The Corinth Canal is 6,343 metres long. Its width amounts to 25 metres, its depth 8 metres and the earth cliffs flanking it reach a maximum height of 63 metres.
Two large bridges – one for railway, and one for the National Road, both of them rebuilt after World War Two – now link Central Greece with the Peloponnese, while below them fairly large ships are piloted directly from one sea to the other. In 1975 a second road bridge was built to ease the increased volume of traffic.
Most reliable yacht charter firms will arrange all paperworks for your crossing through the canal. Instead of sailing the Corinth Gulf, there is the option of sailing around the Peloponese peninsula – compare the northern (Corinth Canal) route and the southern route.
Further reading
- A photographical passage through the canal
- Diolkos [in Greek]
- Protect the sailing in Greece heritage and Sign the petition to save and restore the Diolkos
- The Saronic and Peloponnese area